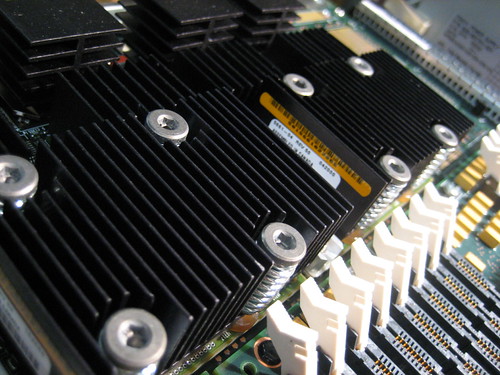
The exponential growth of data generated at the Edge—locations outside of centralized data centers, such as factory floors, remote retail spaces, telecommunications towers, and autonomous vehicles—has created a critical need for high-performance, compact, and energy-efficient computing infrastructure. Traditional server deployments are often too large, power-intensive, and complex for these constrained environments. This imperative has driven manufacturers, particularly Nvidia, to innovate drastically, leading to the development of powerful 2U server architectures specifically engineered to minimize the Edge Footprint while maximizing computational density and efficiency. This shift is not just a technical upgrade; it’s a foundational change enabling the next generation of AI, Internet of Things (IoT), and high-fidelity real-time processing outside the cloud.
Understanding the Challenge of Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source of generation rather than sending it back to a distant cloud or corporate data center. This strategy drastically reduces latency, improves real-time responsiveness, and conserves network bandwidth, all of which are essential for mission-critical applications like predictive maintenance, real-time security analysis, and localized AI inference.
However, the Edge presents unique deployment challenges that contrast sharply with the controlled environment of a data center:
A. Space Constraints and Physical Density
Edge locations (e.g., a small server closet in a retail store or a cabinet on an oil rig) have severely limited physical space. Traditional 4U or 5U servers are often too bulky, demanding maximum performance from the smallest possible form factor, such as a 2U server (approximately $3.5$ inches in height).
B. Harsh Environmental Conditions
Unlike climate-controlled data centers, Edge environments can experience extreme temperature fluctuations, dust, vibration, and humidity. Servers must be ruggedized, capable of operating reliably in conditions far exceeding standard data center specifications.
C. Power and Cooling Limitations
Power delivery and cooling infrastructure at the Edge are typically limited. High-density compute solutions must be power-efficient (optimizing performance per watt) and capable of operating without elaborate HVAC systems, often relying on advanced liquid or passive cooling techniques.
D. Remote Management and Autonomy
Edge servers are often deployed in locations where continuous human oversight is impractical. They require robust remote management, self-healing capabilities, and the ability to operate autonomously, executing AI models and applications without constant cloud connectivity.
The Nvidia 2U Server Architecture: Density Meets AI Power
Nvidia’s solutions for the Edge leverage their core competency in accelerated computing—the use of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) to handle massive parallel processing tasks essential for AI and high-performance data processing. The 2U form factor is the sweet spot for maximizing this acceleration within the physical and thermal constraints of the Edge.
1. Leveraging High-Density GPU Integration
The key to Nvidia’s impact is the ability to pack multiple high-performance Nvidia GPUs (e.g., A100, H100, or specialized Edge cards like the A30) into the tight 2U chassis. This is achieved through highly customized engineering:
- Shorter Card Designs: Using specialized, compact versions of their standard data center GPUs.
- Optimized PCIe Layouts: Maximizing the number of PCIe lanes and slots dedicated to GPUs within the limited physical space, ensuring high-speed data transfer between the CPU and the accelerators.
- Direct-to-Chip Cooling: Employing advanced heat pipe technology or direct liquid cooling plates to manage the intense thermal output of the high-density GPUs within the small chassis volume.
2. The Power of the NVIDIA AI and Networking Stack
The hardware is only part of the solution. The true advantage comes from the seamless integration with the Nvidia software and networking ecosystem.
A. NVIDIA AI Enterprise (NAE)
This software suite provides an end-to-end, cloud-native platform that simplifies the development and deployment of AI applications. It allows developers to containerize AI models and manage them remotely, ensuring the powerful 2U servers can immediately execute inference tasks for complex models without local IT support.
B. NVIDIA Omniverse Integration
For industrial applications, the 2U servers can support the simulation and digital twinning capabilities of Nvidia Omniverse. This allows a remote location (like a factory) to run a simulated model of its operations in real-time, using the local server’s GPU power, enabling localized, optimized decision-making before deploying changes in the physical world.
C. NVIDIA Mellanox Networking
High-performance Edge applications, such as collaborative robotics or multi-sensor fusion in autonomous systems, require extremely low-latency networking. The integration of Mellanox (now Nvidia Networking) technologies, including InfiniBand or high-speed Ethernet NICs (Network Interface Cards), ensures the 2U server can ingest and output massive data streams instantaneously, maintaining the real-time requirements of the Edge.
Use Cases: Transforming Industries at the Edge
The compact, powerful 2U Nvidia servers are catalyzing transformation across several resource-constrained industries by bringing unprecedented compute power out of the cloud.
1. Smart Retail and Autonomous Checkout
In large retail environments, a 2U server can be deployed discreetly in a back room or cabinet.
- A. Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Using computer vision powered by the server’s GPUs to continuously monitor shelf stock, identify misplaced items, and alert staff immediately.
- B. Customer Flow Analysis: Analyzing video feeds to optimize store layout, manage queues, and track shopper paths without sending petabytes of video data back to the cloud.
- C. Enhanced Security: Running complex behavioral analysis AI models locally to identify potential theft or anomalies with near-zero latency, far faster than a cloud-based system.
2. Industrial IoT (IIoT) and Predictive Maintenance
Factory floors and remote industrial sites benefit immensely from the ruggedized, dense computing power.
- A. Visual Quality Control (QC): Utilizing GPU acceleration to run high-speed inspection models, identifying microscopic flaws in manufactured goods (e.g., microchips, textiles) on the production line in milliseconds.
- B. Anomaly Detection: Ingesting sensor data (vibration, temperature, acoustic) from industrial machinery and running deep learning models locally to predict component failure before it occurs, dramatically reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs.
- C. Robotics and Automation: Providing the low-latency processing required for collaborative robots (Cobots) to safely and accurately interact with humans and other machines in real-time.
3. 5G/6G Telecommunications and vRAN
Telco providers are using these compact servers to virtualize their Radio Access Network (vRAN) at cell tower sites, which are inherently space and power-limited.
- A. Virtualizing Baseband Units: Replacing bulky, dedicated hardware with software running on the high-density 2U servers, leading to significant space savings and operational efficiency.
- B. Mobile Edge Computing (MEC): Hosting latency-sensitive applications (like Augmented Reality or cloud gaming) directly on the 5G tower server, ensuring the shortest possible path between the user’s device and the application server.
Powering the Ecosystem: Software and Remote Management 🌐
The long-term viability of the 2U Edge server hinges on its ability to be managed remotely, securely, and efficiently across thousands of dispersed locations.
1. Centralized Fleet Management
Deploying and maintaining thousands of Edge servers requires a unified management plane. Nvidia, along with partners, provides platforms that allow IT teams to:
- A. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Securely push software, AI model updates, and security patches to the entire server fleet simultaneously, regardless of geographic location.
- B. Health and Telemetry Monitoring: Centralized dashboards for real-time monitoring of server health, temperature, power consumption, and GPU utilization, enabling preemptive maintenance.
- C. Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP): Allowing servers to be deployed by non-technical staff. The server connects to the network and automatically downloads its configuration, operating system, and applications from the central management platform.
2. Cybersecurity at the Perimeter
Bringing complex processing to the Edge inherently expands the security perimeter. Nvidia 2U servers are designed with security-first principles:
- A. Root of Trust (RoT): Implementing hardware-based security features that verify the integrity of the boot process, ensuring no malicious firmware or software has been injected before the OS loads.
- B. Secure Execution Environments: Utilizing CPU and GPU features (like Trusted Execution Environments or TEEs) to isolate sensitive AI models and data processing from the main operating system, protecting intellectual property and customer data.
- C. Microsegmentation: Using networking capabilities (e.g., the BlueField DPU) to create granular network security policies within the server, isolating different applications and processes from one another.

The Economic and Environmental Impact
The move to smaller, more powerful 2U servers offers significant economic and environmental advantages that contribute directly to lower operational expenditure (OpEx) and higher profitability, a key concern for large-scale deployments that rely on AdSense and related revenue models.
1. Reduced Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
By increasing the compute density (power per rack unit), organizations need fewer servers and less supporting infrastructure (racks, UPS systems, fire suppression) to achieve the same performance level. This leads to substantial savings in initial equipment purchasing.
2. Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The focus on high power efficiency (performance per watt) inherent in the 2U design translates directly into lower electricity bills—a critical factor for thousands of distributed Edge locations. Furthermore, the remote, autonomous management capabilities drastically reduce the need for expensive “truck rolls” (sending a technician to a remote site) for maintenance and updates, cutting down labor costs.
3. Sustainability and Green Computing
Smaller servers require less raw material to manufacture and their higher energy efficiency reduces the overall carbon footprint of the compute infrastructure. By processing data locally and minimizing the need to transmit everything back to power-hungry, centralized cloud data centers, the solution aligns with modern corporate sustainability goals and reduces the environmental impact of large-scale AI deployments.
Conclusion: The Future is Decentralized and Compact
The advent of highly dense, accelerated computing solutions like the Nvidia 2U servers fundamentally changes the calculus for Edge infrastructure. They address the core constraints of space, power, and environmental robustness, making it feasible to deploy sophisticated AI and high-performance applications far beyond the traditional data center. By effectively shrinking the Edge footprint, these servers empower industries to achieve unprecedented levels of autonomy, efficiency, and real-time responsiveness, paving the way for a truly decentralized and intelligent computing future.